What is Ozone?
Ozone (O3) is Mother Nature’s perfect purifier. The word “ozone” is derived from the Greek word for “smell” and forms naturally in the upper atmosphere. We know it as the ozone layer. It protects us from harmful UV rays. Another form of ozone we are familiar with is a component of air pollution found in the lower atmosphere. We call that bad ozone.
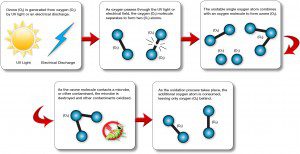
Ozone exists when oxygen (O2) is exposed to ultraviolet light, or exposed to high voltages of lightning. That fresh, clean smell that we notice after a rainstorm, is ozone. It provides a natural, clean disinfectant that can be used in water and air treatment applications. Ozone has been approved by the FDA, USDA, and the EPA as an antimicrobial disinfectant.
As the oxygen molecules (O2) are exposed to these energy fields, they dissociate and split, forming atoms (O1). These wandering oxygen atoms then recombine with other (O2) molecules in the air stream, forming ozone (O3). Ozone is nothing more than another molecular form of oxygen.
Because ozone is highly reactive, it readily oxidizes (breaks down) organic matter. When ozone encounters another compound, one oxygen atom will break away, attach itself to the compound, and oxidize (clean or purify) it.